Ansible Fundamentals
Stefano Morandi
2017-03-04
Created: 2020-09-16 Wed 12:07
Intro
- SCM overview
- Ansible overview
- Ansible components
- Modules / Playbooks / Roles
- Live code session
Software Configuration Management
Server Configuration Management
IT automation tools
SCM is a solution for turning your infrastructure administration into a codebase
competitors
- Puppet
- Chef
- Salt
10.000 lines of handmade bash script- Ansible
SCM benefits
quick provisioning
very fast setup, very fast restore :-D
self-documented procedures
all tasks are described in text files
easy versioning
versioning text file is quite easy
time saving / cost reduction
setup and configure production servers in minutes
Idempotence
Idempotence is the property of certain operations in mathematics and computer science, that can be applied multiple times without changing the result beyond the initial application
\(f(f(x)) = f(x)\)
*

Ansible is..
Ansible is an automation and configuration management technology used to provision, deploy, and manage compute infrastructure across cloud, virtual, and physical environments.
Features
Simple
Everythings is in a simple and human readable YAML files
Powerful
More than 750 modules!
No Magic
All tasks are executed in order
Agentless
Only SSH and python
Ansible is…
automation
Core components
ansible engine
inventory
list of hosts and/or network devices with name, ip address and other variables; can be organized in groups
default /etc/ansible/hosts
Inventory
[web] 10.0.0.100 nginx01.lab.pnlug.lan ansible_host=10.0.2.22 [app] apache[01:99] http_port=8080 [sql] pg[01:99] [all:vars] ansible_user=root
modules
bit of code executed on remote machines
written in many languages (python, bash, powershell…)
returns json
ansible -i hosts all -m ping
ansible -i hosts db01 -m command -a "uptime"
playbooks
playbooks are ansible's configuration language
each playbook is composed of one or more plays in a list
each play is composed of tasks
each task invokes ansible modules
**
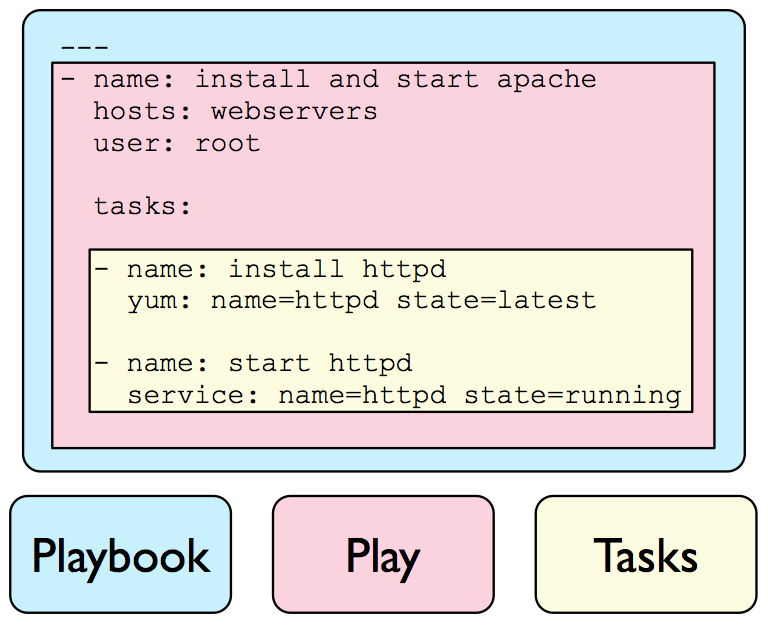
Playbooks
- name: update/upgrade packages
apt:
update_cache: yes
upgrade: safe
tags:
- update
- name: remove puppet packages
apt:
update_cache: no
name: "{{ item }}"
state: absent
with_items:
- puppet
- puppet-common
roles
role is a set of playbooks, templates, files or variables to achieve a specific goal
**
% tree roles
roles
└── mongodb
├── defaults
│ └── main.yml
├── files
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
├── meta
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ └── main.yml
├── templates
└── vars
└── main.yml
Installing
System Requirements
controller
- python 2.7 (python 3.x tech preview from ansible 2.2)
- ssh client
- unix like OS
remote host
- ssh
- python
Installing ansible
# Debian / Ubuntu
apt-get install software-properties-common
apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
# debian
# sed -i "s/jessie/trusty/g" /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ansible-ansible-jessie.list
apt-get update
apt-get install ansible
Installing ansible
# Debian
echo "deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/ansible/ansible/ubuntu trusty main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ansible.list
apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 93C4A3FD7BB9C367
apt-get update
apt-get install ansible
# macOS
brew install ansible
# All :-D
mkvirtualenv -p /usr/bin/python2 ansible
pip install ansible
configuration file
[defaults]
remote_user = root
inventory = hosts.txt
private_key_file = is_rsa_pnlug_ansible
- /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
- $HOME/ansible.cfg
- `pwd`/ansible.cfg
variables
- inventory file
- ansible.cfg
- roles
- playbooks
- command line
16 different places
Examples
ping
$ ansible all -m ping
pnlug-mysql01 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
pnlug-web02 | FAILED! => {
"changed": false,
"failed": true,
"module_stderr": "Shared connection to pnlug-web02 closed.\r\n",
"module_stdout": "/bin/sh: 1: /usr/bin/python: not found\r\n",
"msg": "MODULE FAILURE"
}
pnlug-web01 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
raw
$ ansible -m raw -a "apt-get update" pnlug-web02
$ ansible -m raw -a "apt-get install -y python" pnlug-web02
$ ansible all -m ping
pnlug-mysql01 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
pnlug-web01 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
pnlug-web02 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
apt
$ ansible pnlug-web01 -m apt -a "name=mc state=present"
pnlug-web01 | SUCCESS => {
"cache_update_time": 1488561752,
"cache_updated": false,
==> "changed": true,
"stderr": "",
"stdout": "Reading package lists
...
}
$ ansible pnlug-web01 -m apt -a "name=mc state=present"
pnlug-web01 | SUCCESS => {
"cache_update_time": 1481102874,
"cache_updated": false,
==> "changed": false
}
apt
$ ansible pnlug-web02 -m apt -a "name=mc state=absent"
pnlug-web02 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"stderr": "",
"stdout": "Reading package lists...",
...
"update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.tiny to provide /usr/bin/view (view) in auto mode",
"Processing triggers for mime-support (3.59ubuntu1) ..."
]
}
$ ansible pnlug-web02 -m apt -a "name=mc state=absent"
pnlug-web02 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false
}
information gathering
$ ansible pnlug-web02 -m setup
pnlug-web02 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.25.105"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [
"fe80::746a:d8ff:fec7:e576"
],
"ansible_architecture": "x86_64",
"ansible_bios_date": "11/09/2013",
"ansible_bios_version": "J06",
...
"ansible_os_family": "Debian",
...
"ansible_virtualization_role": "guest",
"ansible_virtualization_type": "lxc",
...
}